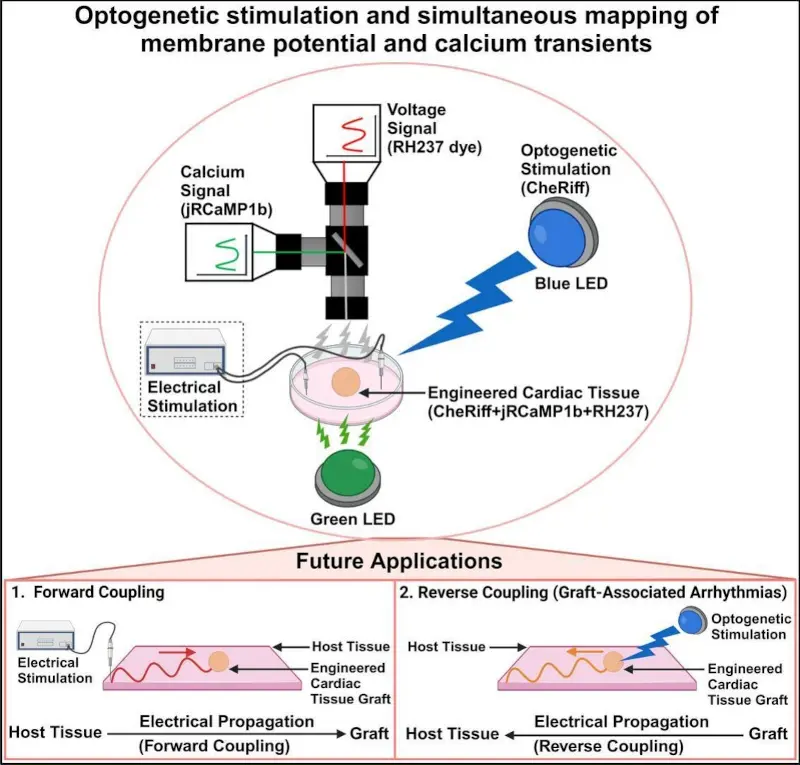
Cardiac Spheroids : Simultaneous Optical Mapping of Membrane Potential and Calcium Transients
Cardiac Spheroids: High Physiological Relevance in 3D
Cardiac spheroids (or organoids) created from human iPS cells (hiPSCs) are miniature models in which cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, etc. self-organize to form a 3D structure.
-
Biologically relevant tissue architecture
Cells interact in a 3D environment, reproducing human-specific cardiac tissue maturation and disease processes with high precision -
Improved predictive power
Demonstrates higher physiological relevance than traditional 2D models for drug discovery, toxicity testing, and disease modeling -
Flexible design
By using iPSCs derived from patients with specific diseases, the system enables personalized therapy development and modeling of disorders with defined genetic backgrounds, such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy.
Innovative “All-Optical” Electrophysiology Platform
Recent research has established an "all-optical" method that combines optogenetic stimulation with simultaneous optical mapping of membrane potential (Vm) and calcium transients (CaT), and this approach has been applied to cardiac spheroids.
Below is an example of human iPSC-derived cardiac spheroids labeled with a voltage-sensitive dye (RH237) and a calcium-sensitive fluorescent protein (jRCaMP1b), recorded simultaneously using two high-speed cameras in perfect synchronization.
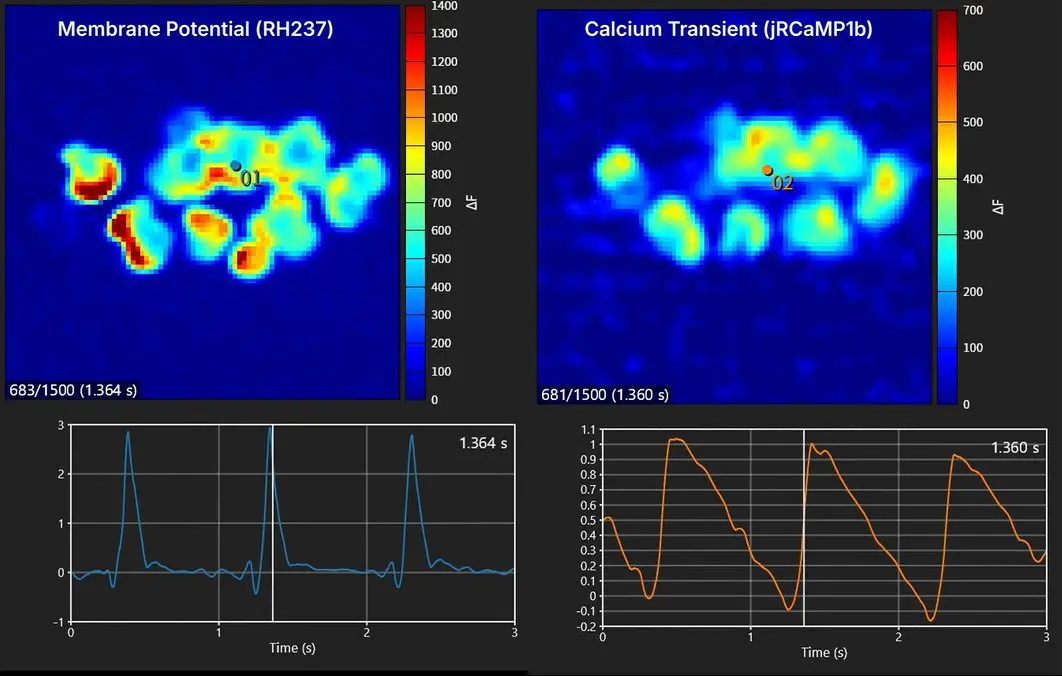
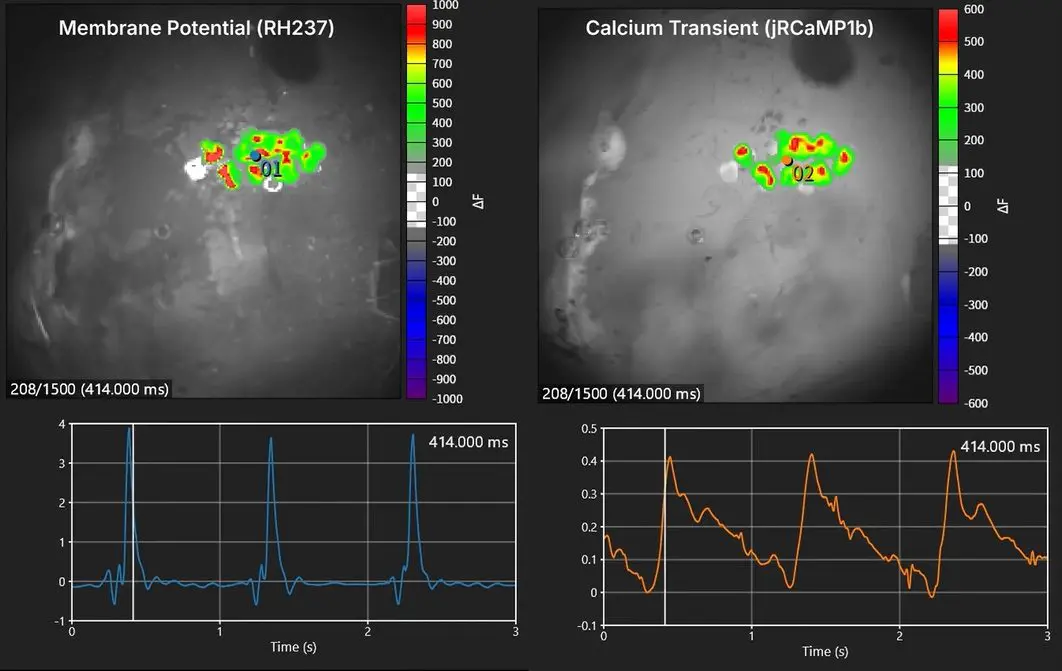
Simultaneous mapping of membrane potential and calcium using human iPS cell-derived cardiac spheroids
-
Non-invasive and high-precision recording
Eliminates noise from electrical stimulation and avoids physical interference from electrodes, enabling millisecond-resolution imaging of cardiac electrophysiology -
High-precision visualization
Enables direct imaging of cardiac electrophysiological function with high spatiotemporal resolution compared with conventional electrical mapping. -
Integrated understanding of excitation-contraction coupling
Simultaneous recording of Vm and CaT from the same sample provides richer insights into cardiac function and arrhythmia mechanisms -
Independent stimulation
With optogenetic actuators (such as CheRiff) expressed only in the graft, stimulation can be applied without affecting host tissue
Sample data
- Sample
- Human iPS cell-derived cardiac spheroids
- Method
- Electrical Stimulation
- Fluorescence Probes
-
Voltage sensitive dye (RH237, left image)
Genetically Encoded Calcium Indicator (jRCaMP1b, right image) - Imaging System
- MiCAM03-N256 Dual Camera System
- Pixels
- 256x256
- Frame Rate
- 500fps (2.0msec/frame)
- Data provided by
-
Dr. Hanyu Zhang, Dr. Bijay Guragain. Dr. Jianyi Zhang,
and Dr. Jack M. Rogers
Department of Biomedical Engineering
The University of Alabama at Birmingham - Reference paper
-
Optogenetic stimulation and simultaneous optical mapping of
membrane potential and calcium transients in human engineered
cardiac spheroids
Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 199 (2025) 51-59
Related Products
The following optical mapping system is primarily based on the high-speed camera MiCAM03-N256, which was used to capture the video above.
It captures and images the electrical activity of fluorescently stained cardiac and neural samples at high speeds of up to 1,818 frames per second at full resolution, and supports everything from image and waveform analysis to map image creation and export. It also comes with a high-powered LED light system and electrical stimulator, both of which are necessary for data collection. This is an all-in-one turnkey system that allows you to start experiments right away.
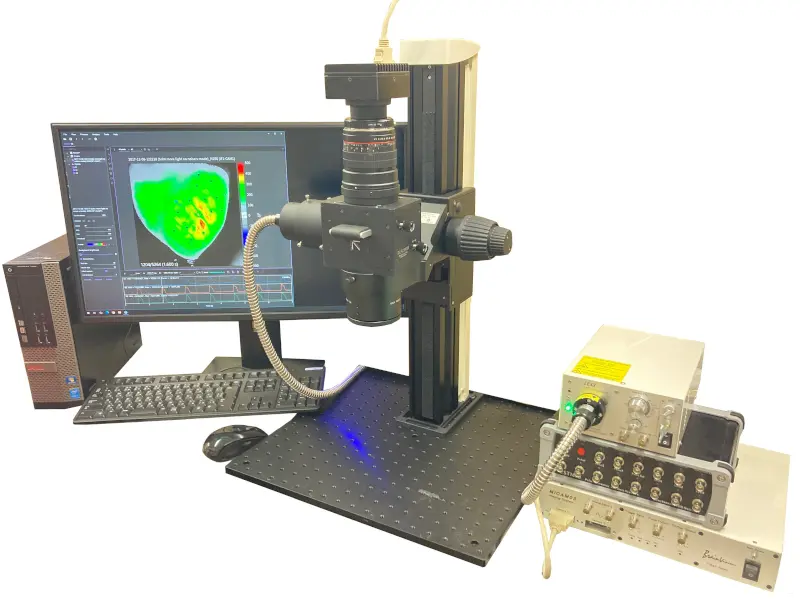
High-speed optical mapping system
Main Applications
- Membrane potential imaging using voltage-sensitive dyes and GEVIs (genetically encoded voltage indicators)
- Calcium imaging using calcium dyes and GECIs (genetically encoded calcium indicator)
- Ratio imaging using two cameras
Components and Features
- Number of pixels: 256x256 to 32x32 pixels
- Maximum frame rate: 1,818fps (256x256 pixels), 20,000fps (32x32 pixels)
- Analog signal recording such as ECG, pulse output, light source lighting signals, etc. are possible. Synchronization with external devices is also easy.
- Comprehensive map generation functions, including activation maps and conduction velocity maps
- Intuitive and easy-to-use interface, reducing analysis time
- Export of high-resolution images suitable for publications and presentations
- Despite its low magnification (approximately 0.19x to 6.3x), "THT Mesoscope" provides brighter observation than conventional fluorescence microscopes
- Improved signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) for high-speed fluorescence imaging
- Simultaneous dual-wavelength measurement possible using a fluorescence splitter
- High-brightness illumination improves imaging S/N ratio
- High stability ensures no additional noise is introduced into biological signals
- Supports pulse output, analog input, oscilloscope functionality, and light source trigger control
- Built-in stimulus isolator allows immediate stimulation simply by connecting electrodes
History and Achievements
Over 27 years since its release, approximately 430 units have been installed in 230 neuroscience and cardiovascular research institutions worldwide. The MiCAM series is recognized as the standard system for high-speed membrane potential imaging.
Approximately 1,000 academic papers using our products have been published over the past 27 years.
Contact Us
For inquiries regarding the introduction of a cardiac spheroid mapping system, as well as detailed specifications and pricing of the mapping system, please contact us using the button below.
We are happy to provide suggestions to help further advance your research.
[2] Cardiac organoids: a new tool for disease modeling and drug screening applications. Front Cardiovasc Med . 2025 May 20:12:1537730.